How Much Weight Can You Lose With Lap Band Surgery
How much weight can you lose with lap band surgery. Surgery can lead to significant weight loss and improve health. However, there is also a risk of sometimes serious complications. After the procedure, you also have to change a lot in order to avoid digestive problems and deficiency symptoms. Therefore, good care after the operation is important.
How much weight will I lose?
A: Weight loss results vary from patient to patient, and the amount of weight you lose depends on several factors. The band must be in the correct position and you have to commit to your new lifestyle and your new eating habits. Obesity surgery is not a miracle cure, and pounds don’t go away on their own. It is very important that you set achievable weight loss goals from the beginning.
It is possible to achieve a weight loss of 2 to 3 pounds a week for the first year after the operation, but you will most likely lose a pound a week. Generally, 12 to 18 months after the operation, losing weight too fast creates health risks and can lead to a number of problems. The main objective is to achieve a weight loss that prevents,
How do the weight loss results of the lap-band system compare to the results of gastric bypass surgery?
A: Surgeons have reported that gastric bypass surgery patients lose weight faster in the first year. By five years, however, many LAP-BAND patients have achieved weight loss similar to that achieved by patients undergoing gastric bypass surgery.
Focus on long-term weight loss and remember that it is important to do so gradually while reducing obesity-related risks and improving your health.
Surgery to treat obesity
For people with severe obesity or comorbidities such as diabetes, surgery may be an option to lose a lot of weight in a short period of time – for example, a stomach reduction. Such interventions are called bariatric operations (from “baros”, Greek: weight) or obesity operations. Suctioning off body fat is not a treatment option for obesity, as it has little impact on calorie intake and consumption and is associated with risks. In addition, it has not been shown to improve health.
According to the current recommendations of the medical societies, an operation is an option if
- the BMI is over 40 (obesity grade 3) or
- the BMI is between 35 and 40 (obesity grade 2) and there are also other diseases such as diabetes, heart disease or sleep apnea.
As a rule, however, an intervention is only considered if other attempts to lose weight were unsuccessful – for example, if an accompanied weight loss program with nutritional advice and exercise did not result in sufficient weight loss. For some people, an operation can also be useful without first attempting to lose weight, for example one BMI over 50 or severe comorbidities.
When deciding for or against an intervention, it is important to carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages. Obesity surgeries can lead to significant weight loss, improve health and quality of life. They also have a beneficial effect on comorbidities, especially diabetes, Sleep apnea and high blood pressure. But they can also lead to various complications and have lifelong effects. In addition, if you lose weight very quickly, you must expect gallstones to form.
Following the procedure, long-term lifestyle changes, such as diet, and regular check-ups are required. Many people regain weight easily several years after having obesity surgery.
How can surgeries help with obesity?
Various gastric surgeries can be used to treat obesity. The most commonly used procedures are:
- The gastric band : The stomach is tied up with an elastic band so that it can no longer absorb as much food and you are full more quickly. This intervention can be reversed.
- the sleeve gastrectomy (stomach stapling) : Here, the stomach is surgically reduced, in order to reduce its capacity.
- of gastric bypass : This will be shortened in addition to stomach stapling of the digestive tract, so that the body less nutrients and calories can absorb from food.
Gastric bypass and gastric sleeve surgery also cause hormonal changes that curb appetite and influence the metabolism, which also has a beneficial effect on diabetes.
The weight loss has made many people feel physically fitter after the procedure. Exercise and sport are easier and more fun again. After the operation, many receive positive and beneficial feedback from those around them. Some people also report that since their operation they feel more resilient and sexually fulfilled again at work.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a gastric band?
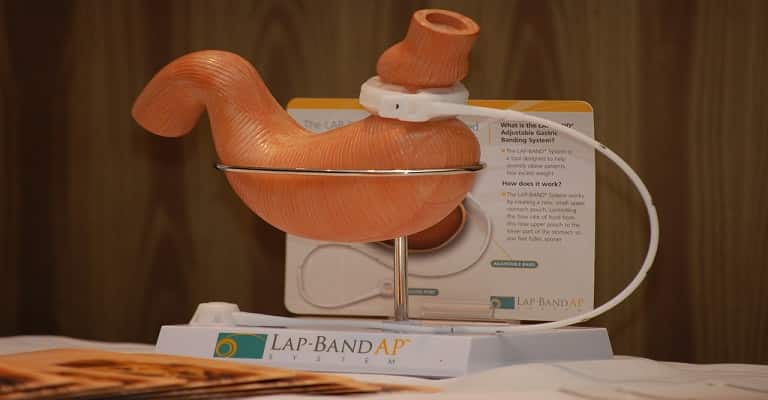
A gastric band compresses the stomach and artificially makes it smaller. It is made of silicone and is placed around the entrance of the stomach in a ring. This creates a small forestomach that can no longer take in so much food, so that you feel full more quickly.
Gastric banding: the least intrusive surgical procedure
The gastric band is filled with a saline solution and can therefore be made narrower or wider after the operation: liquid can be drained or added through a tube with the aid of a syringe. The access to it (port) is attached under the skin and is about the size of a coin. For example, if you vomit because the gastric band is too tight, you can keep it up.
A gastric band is the least intrusive surgical procedure. Because the stomach and digestive tract are otherwise unchanged, there are fewer problems absorbing nutrients. It is also possible to remove the gastric band again, thereby reversing the procedure. It is therefore a sensible alternative, especially for young women who want to have children. However, sometimes you canAdhesions make it difficult to remove the gastric band.
Typically, body weight is reduced by around 10 to 25% in the first year after inserting a gastric band. A man who is 1.80 meters tall and 130 kilograms can lose 10 to 30 kilograms in weight. In the second and third year after the procedure, the weight can still decrease a little.
In comparative studies, gastric banding was less effective than gastric sleeve surgery or gastric bypass surgery. Sometimes the weight loss is not enough. Then the gastric band can be removed and gastric-reducing surgery can be considered.
Possible side effects of a gastric band include heartburn and vomiting, for example if the gastric band is too tight. The gastric band can also slip, grow in, or tear. Sometimes it has to be replaced or removed as a result. In studies, around 8 out of 100 people who had gastric band surgery developed a complication. Up to 45 out of 100 people will have reoperations at some point – for example because they have not lost enough weight or a problem with the gastric band has occurred.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of gastric sleeve surgery?
With a stomach reduction, about three quarters of the stomach are surgically cut off and removed. Because the shape of the stomach then resembles a tube, the procedure is sometimes called a gastric sleeve surgery.
Sleeve stomach surgery
After a stomach reduction, people who are obese typically lose around 15 to 25% of their weight in the first year. For a man who is 1.80 meters tall and weighs 130 kilograms, this would mean that he can expect a weight loss of a good 20 to 30 kilograms after the operation.
A stomach reduction can have various side effects: If you have eaten too much, you may experience heartburn or vomiting. Complications can arise during or after the operation: For example, the surgical sutures in the stomach can become leaky and require further surgery. In studies, around 9 out of 100 people had a complication during or after surgery; 3 out of 100 had to be reoperated. Less than 1 in 100 people died from surgery or complications.
A stomach reduction is irreversible. If a person with obesity has not lost enough weight after gastric sleeve surgery, an additional intervention is possible later, such as a gastric bypass.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of gastric bypass?
Gastric bypass is more time-consuming and complicated than gastric banding or gastric sleeve surgery. The name is derived from the English term “bypass“(Bypassing), because the food then no longer travels through the entire stomach and small intestine, but is mostly led past them.
During the operation, a small part of the stomach (about 20 milliliters) is cut off. This then forms a pocket that connects to theSmall intestineis connected. The rest of the stomach is sewn shut and is no longer connected to the esophagus. The food then passes directly from the gastric pouch that has formed into theSmall intestine.
So that the digestive juices from the gallbladder, pancreas and the remaining stomach can continue to get into the intestine, the upper Small intestine at another place at the gastric outlet Small intestine connected.
Gastric bypass
Similar to stomach surgery, studies show that obese people typically lose around 15 to 25% of their weight in the first year after gastric bypass surgery. This happens relatively quickly. The weight usually levels off one to two years after the procedure.
According to current knowledge, gastric bypass leads to greater weight loss in the long term than the other procedures. Gastric bypass is particularly beneficial for comorbidities such as .
Side effects and operational risks
Two common long-term consequences of gastric bypass are early and late dumping syndromes. With early dumping syndrome, a large amount of undigested food quickly gets into the Small intestine. The body tries to “dilute” the unusual amount of nutrients and suddenly a lot of water flows from the blood vessels into the Small intestine. This fluid is then absent from the bloodstream and blood pressure falls. This can lead to drowsiness, nausea, stomach pain and sweating. An early dumping syndrome occurs mainly after eating very sugary foods, usually within 30 minutes of it.
In the rarer late dumping syndrome, the body is getting too much insulin released what became a Hypoglycaemiawith typical complaints such as dizziness, weakness and sweating. It can occur one to three hours after eating, especially after consuming high-carbohydrate foods.
The surgical risks include scarring in the Small intestine, internal hernias and leaky sutures at the new joints between the stomach and intestines. All of these complications can require further surgery. In studies, 12 out of 100 people had a complication; 5 out of 100 people had to be operated on.
Life-threatening complications rarely occur during the operation or in the first few weeks afterwards. For example, blood poisoning can occur if one of the new connection points leaks and stomach contents enter the abdomen. In studies, fewer than 1 in 100 people died during surgery or from complications from gastric bypass surgery.
How is the operation prepared?
In the weeks leading up to surgery, it is often recommended that you lose some weight through diet or medication. This is supposed to simplify the operation itself, among other things because it shrinks the liver somewhat and makes it easier to operate at the junction between the esophagus and stomach.
Various tests will be done before the operation to make sure that there are no medical reasons against it. This includes various laboratory tests, a gastroscopy and an ultrasound of the abdomen. A psychological examination can also be useful – for example, if there is an eating disorder that may have psychological reasons.
Which surgery is suitable for me and how does it work?
Which operation is considered depends on your own expectations and your personal assessment of the advantages and disadvantages, among other things, on the state of health, weight and possible accompanying diseases. The professional activity can also play a role in the decision. It makes sense to seek treatment from doctors who are experienced in the method used. Treatment centers that are certified by the German Society for General and Visceral Surgery (DGAV) for obesity surgery meet special requirements for experience and equipment with these treatments.
Obesity operations are now performed endoscopically (minimally invasive). In minimally invasive surgery, the operation is carried out with the help of special endoscopes that are inserted into the abdominal cavity through several small incisionslaparoscopy). Open surgeries are no longer common.
A hospital stay of a few days is usually necessary for minimally invasive surgery.
How do I have to change my life after the operation?
After the operation, you may have to avoid solid food for a few weeks. Depending on the procedure, you initially only eat liquid (for example water and broth) and then with soft food (for example yogurt, mashed potatoes, mashed potatoes). After a few weeks, solid foods are gradually introduced to slowly get the stomach and intestines used to it again.
After the surgery, nutritional advice is important to avoid digestive problems such as heartburn, stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. Depending on the type of surgery, it may be necessary
- to eat small portions ,
- to eat slowly and chew well,
- not to drink and eat at the same time , as the stomach does not have enough capacity for both. It is recommended not to drink in the 30 minutes before and after eating.
- Avoid foods rich in fat and sugar as they can lead to digestive problems. Especially after gastric bypass surgery, foods high in sugar can lead to severe side effects due to dumping syndrome. These include, for example, sweets, fruit juices, cola and ice cream.
- Drink alcohol in moderation , as the body may absorb it much faster. This is especially true after gastric bypass surgery.
Nutrient supply after the operation
After obesity surgery, especially gastric bypass surgery, the digestive tract can Vitamins and no longer absorb nutrients so well. To prevent deficiency symptoms, it is necessary to take food supplements for life. These include, for example calcium and vitamin D to maintain bone substance and before osteoporosis to protect – but also vitamin B12, Folic acid, Iron, selenium and zinc, which are necessary for blood formation and the immune system, among other things .
To protect against deficiency symptoms, regular blood tests are also recommended, initially after six months and later once a year. There are fewer with a gastric band Food supplements necessary than with gastric sleeve and gastric bypass.
There is also the risk that the body will also lose muscle mass in addition to fat. To prevent this, it is recommended that you eat a high-protein diet and exercise regularly after the operation.
Cosmetic consequences
The severe weight loss often leads to sagging skin. The skin folds and drooping skin flaps are perceived by many as unsightly and stressful. Some would like to have their skin tightened afterwards, but the health insurances will only pay for it in the event of medical problems or severe psychological stress. For example, large skin folds can lead to infections or rashes. Good skin care is therefore important. A separate application must be made to cover the costs of an operation to tighten the skin.
Who can I talk to before I make up my mind?
Obesity surgery is a major procedure that requires long-term changes in life and daily life. So before you decide to do it, it makes sense to do some research on the consequences. A list of questions can help prepare for the counseling sessions.
It is best to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the various surgical procedures as well as the changes after the operation with specialists who are well versed in the treatment. These include experienced nutritionists, nutritionists and specialized medical practices, psychotherapists and clinics in obesity surgery. Self-help groups can help, for example, to answer questions about submitting an application to the health insurance company.
Possible questions are, for example:
- Is an operation an option for me and if so, which one?
- What are the risks and side effects and how common are they?
- How good are the chances of success? How often do you have to re-operate?
- What weight loss can I expect after the procedure?
- What Health Benefits Can I Expect?
- How do I have to change my diet after the operation?
- Which foods may I no longer tolerate as well after the operation?
- Which Food supplements do I need to meet my nutritional needs after the operation?
- How often are check-ups necessary after the operation?
- Who will look after me after the operation?
People do not always receive the support and advice they need before and after an operation. This can lead to false expectations and then to problems in everyday life. Self-help organizations can help find support options.
What should you watch out for if you want to have children?
Basically, a woman can become pregnant and have a healthy child after obesity surgery . If you want to have children, however, it is important to talk to your doctor about possible risks – for example, whether additional examinations or Food supplementsare necessary to avoid possible deficiency symptoms. Pregnancy is generally not recommended in the first twelve months after an operation, as the body loses a lot of weight during this time and the unborn baby would not get enough nutrients.
Will my health insurance company pay for gastric surgery?
In principle, the statutory health insurance companies can cover the costs of an obesity operation. To do this, an application must first be submitted with the doctor, including a medical certificate. In order for the operation to be approved, certain requirements must be met:
- The surgery is medically necessary and other treatment options have been tried without sufficient success.
- Treatable diseases that lead to severe obesity were excluded. This applies, for example, to an underactive thyroid or an overactive adrenal cortex.
- There should be no important medical reasons against it. These include, for example, health problems that make surgery too risky; a pregnancy; drug or alcohol addiction and severe mental illness that can make it difficult to make lifestyle adjustments after an operation.
You also have to show willingness to exercise enough and eat healthily after the operation. To do this, you usually add a letter of motivation and various documents to the application for reimbursement of costs. This includes, for example, certificates of participation in weight loss programs or nutritional advice, a food diary and certificates of participation in sports courses.